Primary packaging plays a crucial role in the pharmaceutical industry as it directly impacts the safety, efficacy, and stability of pharmaceutical products. Its primary function is to make direct contact with the medication, providing a protective barrier against environmental contaminants and preserving the product’s shelf life.
What is Primary Packaging
Primary packaging is the first and most critical layer of protection in pharmaceutical packaging. It is the material that directly interacts with the medication, and its principal role is to protect the medication against physical, chemical, and biological contamination.w
The integrity of pharmaceutical products is paramount, and primary packaging is at the forefront of maintaining this integrity. It protects against physical, chemical, and biological contamination. Furthermore, the packaging must be inert so that it does not interact with the medication, ensuring that the drug’s therapeutic properties are not altered until administered.
Types of Primary Packaging
Primary packaging is the first layer of protection for a product, and it comes in various forms. Some common types of primary packaging include:
Bottles: Glass or plastic bottles are widely used for packaging liquids, such as pharmaceuticals, beverages, and cosmetics. They provide a secure seal to prevent contamination and preserve the product’s integrity.
Cans: Metal cans are used for packaging food, beverages, and other products that require airtight sealing. They offer excellent protection against light and oxygen, ensuring the product’s shelf life.
Jars: Glass jars are often used for packaging food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals that require a sterile environment. They are ideal for products that need to be kept free from contaminants.
Containers: Plastic or metal containers are versatile and used for packaging a wide range of products, including food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. They provide robust protection and are available in various sizes and shapes.
Labels: Labels are an integral part of primary packaging, providing essential information about the product, such as ingredients, instructions, and branding. They ensure that consumers have all the necessary details at their fingertips.
Importance of Selecting the Right Primary Packaging
Selecting the right primary packaging is crucial for ensuring the safety and quality of the product. Factors to consider when selecting primary packaging include:
Compatibility: The packaging material should be compatible with the product to prevent contamination or degradation. For instance, certain medications may require specific materials that do not react with their chemical composition.
Barrier Properties: The packaging material should provide a sufficient barrier to protect the product from external factors, such as light, moisture, and oxygen. This is essential for maintaining the product’s efficacy and shelf life.
Sterility: Primary packaging for pharmaceuticals and medical devices requires sterility to prevent contamination. Ensuring that the packaging is sterile is vital for patient safety.
Sustainability: Eco-conscious consumers are increasingly demanding sustainable packaging options, such as recyclable materials and minimal packaging. Companies must consider the environmental impact of their packaging choices and opt for materials that can be recycled or have a lower environmental footprint.
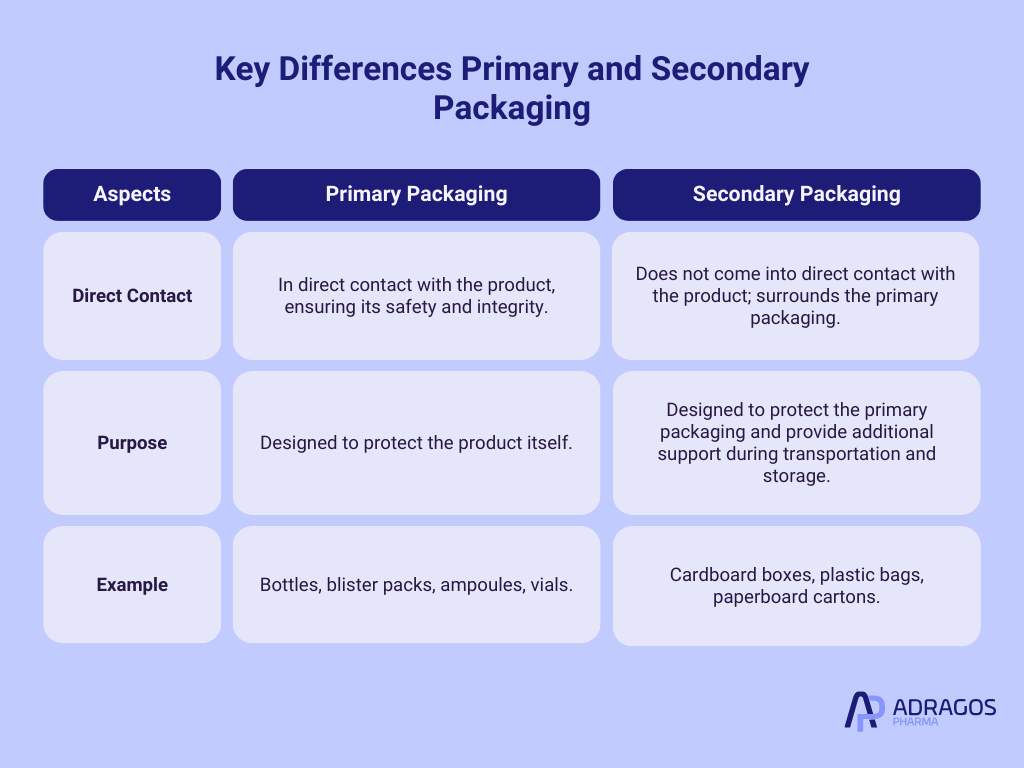
Primary and Secondary Packaging: Understanding the Difference
Primary packaging is the first layer of protection for a product, while secondary packaging is the outer layer that provides additional protection and support. The main differences between primary and secondary packaging are:
- Direct Contact: Primary packaging is in direct contact with the product, ensuring its safety and integrity. In contrast, secondary packaging surrounds the primary packaging and does not come into direct contact with the product.
- Purpose: Primary packaging is designed to protect the product itself, while secondary packaging is designed to protect the primary packaging and provide additional support during transportation and storage.
Examples of secondary packaging include cardboard boxes, plastic bags, and paperboard cartons. These materials help group individual units together, making them easier to handle and transport.
Materials Commonly Used in Primary Packaging
Choosing the right materials for primary packaging is critical to ensuring product safety and stability. Typical materials include glass, high-density polyethylene (HDPE), and polypropylene. Each material is selected based on its ability to provide adequate protection against specific environmental threats, such as moisture and oxygen, and its compatibility with the pharmaceutical product.
Compliance and Regulatory Standards
Pharmaceutical primary packaging must adhere to strict regulatory standards set by global and local health authorities. These regulations ensure that packaging is safe for use, does not interact with the product, and protects the medication up to its intended shelf life. Our facilities, including the Adragos Kawagoe facility in Japan, are designed to meet these stringent standards, ensuring that all products are compliant with international and Japanese pharmaceutical regulations.
The Role of Packaging in the Supply Chain
Packaging plays a critical role in the supply chain, serving multiple purposes, including:
Protection: Packaging protects the product from damage during transportation and storage. It ensures that the product reaches the consumer in perfect condition.
Identification: Packaging provides information about the product, such as ingredients, instructions, and branding. This helps consumers make informed decisions and ensures regulatory compliance.
Marketing: Packaging can be used as a marketing tool to promote the product and attract consumers. Eye-catching designs and informative labels can enhance the product’s appeal on retail shelves.
Logistics: Packaging can affect the efficiency of logistics operations, such as storage, transportation, and handling. Well-designed packaging can optimize space and reduce costs in the supply chain.
Specialized Packaging at Adragos Kawagoe
Our Adragos Kawagoe site in Japan exemplifies our commitment to innovative and secure pharmaceutical packaging solutions. This facility is specifically equipped to meet the precise packaging needs of the Japanese market, adhering to both local and international standards. The focus is on using advanced packaging technologies and materials that ensure the safety and integrity of every packaged product.
Our facilities are equipped to handle the packaging needs of solid dosages, with a capacity for up to 162.5 million tablets, as well as injectables, including an integrated process from formulation to packaging for ampoules in various sizes—1, 2, 5, 6, 10, or 50 ml.


Technological Innovations in Primary Packaging
Advancements in primary packaging technology have significantly improved the efficiency and safety of pharmaceutical packaging. These include the development of primary packaging machines that ensure accuracy and integrity in packaging processes, and the introduction of new materials and designs that further protect and preserve pharmaceutical products.
Packaging and Sustainability
Packaging has a significant impact on the environment, and consumers are increasingly demanding sustainable packaging options. Some ways to make packaging more sustainable include:
Using Recyclable Materials: Opting for materials such as cardboard and paperboard that can be easily recycled helps reduce waste and environmental impact.
Minimizing Packaging Waste: Using minimal packaging designs that reduce excess material can significantly cut down on waste. This approach not only benefits the environment but also reduces costs.
Using Biodegradable Materials: Incorporating biodegradable materials, such as bioplastics and compostable packaging, can help reduce the long-term environmental impact of packaging waste.
Designing for Reuse: Creating packaging that can be reused, such as refillable containers, appeals to eco-conscious consumers and promotes a circular economy.
By considering sustainability in packaging design, companies can reduce their environmental impact and appeal to eco-conscious consumers, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable future.
The Critical Role of Primary Packaging in Product Stability and Shelf Life
Primary packaging is not only about compliance and protection but also about maintaining the stability and efficacy of pharmaceutical products throughout their intended shelf life. Proper packaging ensures that medications are effectively protected from production through to delivery, ultimately ensuring patient safety.
The importance of primary packaging in the pharmaceutical industry cannot be overstated. It is the first and most critical barrier that protects the product’s quality, safety, and efficacy. At Adragos, we are dedicated to providing the highest standards of primary packaging solutions that meet the rigorous demands of the pharmaceutical industry, ensuring that every product delivered is safe and effective.
FAQs on Primary Packaging
What is secondary packaging?
Secondary packaging is the additional packaging that surrounds the primary packaging, often used to group larger quantities of the product for shipping and handling.
What is primary vs secondary packaging marketing?
In marketing, primary packaging focuses on the consumer’s direct interaction with the package, while secondary packaging is used primarily for logistical purposes and may also serve to provide additional protection.
What are the four types of packaging?
The four main types of packaging are primary, secondary, tertiary (or transit packaging), and quaternary, which is used for bulk handling and warehouse storage.
What is primary packaging classification?
Primary packaging classification refers to categorizing packaging based on its direct contact with the product, materials used, and the type of packaging such as bottles, blister packs, and ampoules.
What is tertiary packaging?
Tertiary packaging is the outermost layer designed for safe transportation and handling of products. It protects secondary packaging during shipping, ensuring products remain intact through various transit points. Tertiary packaging is typically discarded before reaching the consumer and is crucial for reducing costs and enhancing efficiency in the shipping process.
