Table of Contents
The pharmaceutical industry constantly deals with medicines that require precise preparation for safe patient administration. Among these processes, sterile compounding is an essential practice that is performed to ensure patient safety, prevent infection, and maintain medication effectiveness. Within the scope of sterile compounding, one specific technique stands out for its effectiveness and assurance of sterility—aseptic compounding, which involves the careful handling and transfer of drug solutions to prevent microbial contamination and ensure compatibility.
Understanding Aseptic Compounding
Aseptic compounding refers to the meticulous process of preparing medications under strictly sterile conditions, ensuring complete absence of contamination from pathogens, including bacteria and fungi. This procedure is essential particularly when medicines are administered intravenously, as topical ophthalmic solutions, inhaled solutions, or in injections directly entering patients’ circulatory systems. Understanding the various components involved in aseptic compounding, including practice standards, regulations, and essential procedures, is critical for ensuring safety and compliance in the medication preparation process.
The primary goal of aseptic compounding is to maintain medication sterility throughout compounding, packaging, and administration, safeguarding patients from possible infections and cross contamination. This requires a controlled area, classified according to airborne particles grade as outlined in regulatory guidelines, to minimize contamination risks during the preparation of sterile medications.
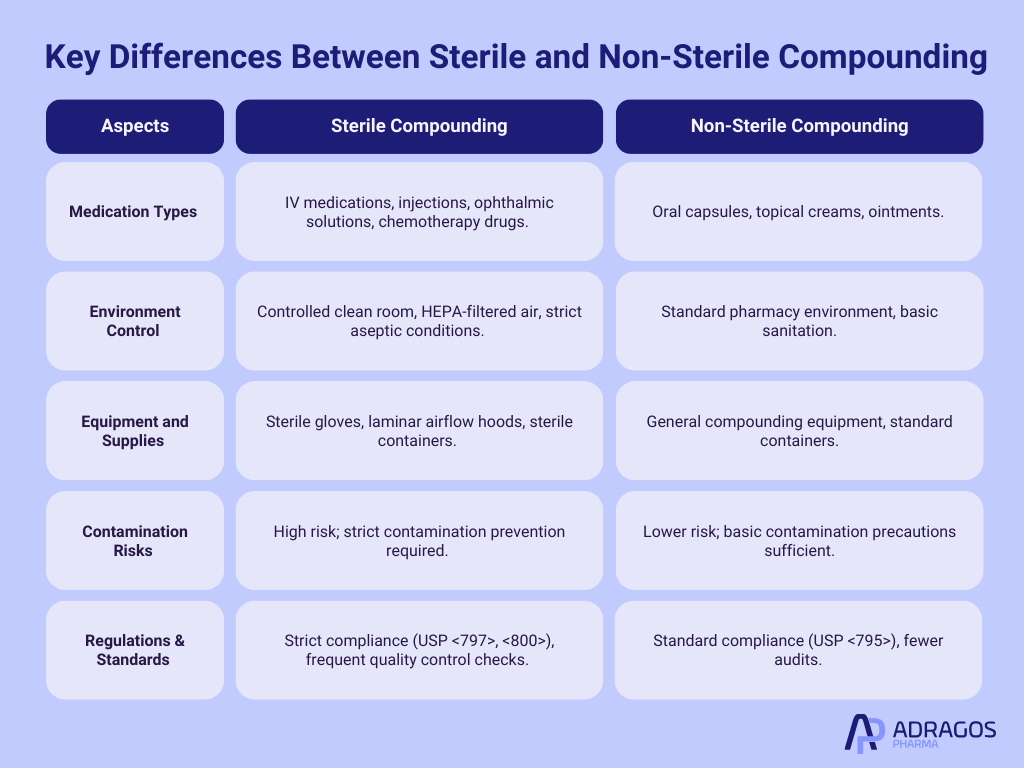
Key Differences: Sterile Compounding vs. Non-Sterile Compounding
Unlike non sterile compounding, which deals with topical creams, oral capsules, and other less sterile-dependent medications, sterile compounding specifically supports intravenous medications, injections, antibiotic solutions, chemotherapy drugs, and ophthalmic preparations. When compared to non-sterile compounding, the critical difference is the rigorous and controlled environment necessary to prevent contamination in sterile compounding.
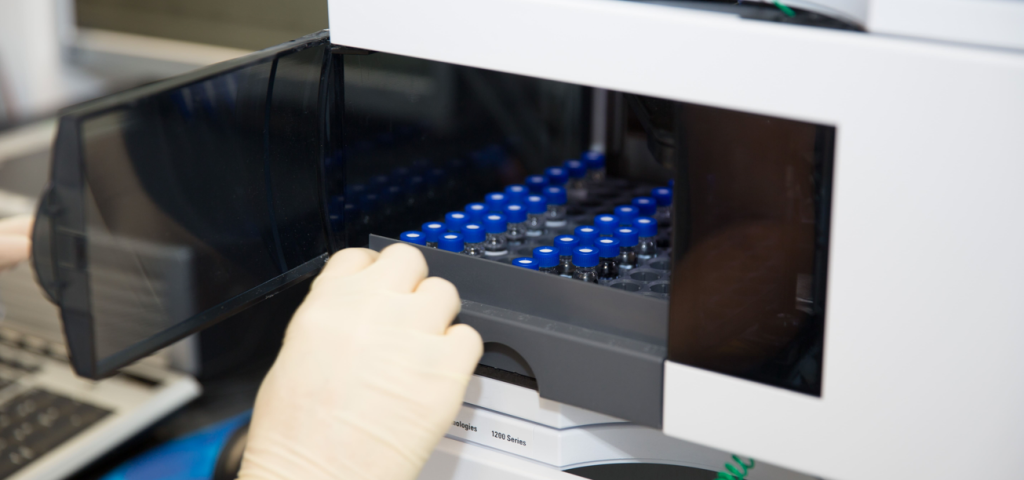
Importance of Aseptic Compounding Technique in Pharmacy
Implementing proper aseptic technique is essential in pharmacy practices concerning sterile preparation. It includes meticulously followed procedures, specialized equipment, sterile supplies, and a strictly controlled environment to assure medication sterility. It helps pharmacy technicians and pharmacists prevent contamination and deliver medicines of the highest quality to patients and hospitals.
Essential Elements of Aseptic Compounding Technique
The aseptic technique is guided by five essential principles:
- Good personal hygiene and gowning procedures, including sterile gloves
- Proper cleaning and disinfecting of hands and surfaces
- Using laminar airflow hood and HEPA filter systems for sterile compounding
- Minimizing exposure and handling to avoid cross contamination
- Ensuring appropriate sterilization of compounding supplies and equipment prior to use
Equipment and Environment for Aseptic Compounding
Compounded sterile preparations are typically prepared in designated controlled area settings, such as a clean room. A suitable clean room environment includes temperature, humidity, and pressure controls managed carefully to meet strict standards. The underlying objective is eliminating contamination risk via controlled air and sterile surfaces.
A proper aseptic compounding environment involves key equipment including:
- Laminar airflow hood
- HEPA filters
- Biological indicators
- Sterilized mixing tools and plastic containers
- Sterile gloves and gowns
- Properly maintained sterile surfaces
Additionally, proper disposal methods for hazardous drugs and materials such as syringes, cytotoxic agents, and radiopharmaceuticals are crucial to prevent contamination and protect healthcare workers.
Regulatory Compliance and Guidelines for Aseptic Compounding
To ensure consistency and safety, aseptic compounding significantly relies on compliance with standards from the United States Pharmacopeia (USP), especially USP <797> and <800>. Regulations and guidelines define minimum requirements for facilities, training, procedures, testing, practices, and continuous monitoring to maintain the highest standards.
Quality Assurance and Quality Control in Aseptic Compounding
Quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) are fundamental aspects of sterile compounding. Validation processes are intended to ensure consistent quality and compliance. Quality assurance programs monitor facilities, equipment, compounding procedures, pharmacy technicians’ performances, and pharmacists’ adherence to guidelines. Quality control testing ensures compounded sterile preparations meet predefined criteria for sterility, potency, purity, and stability before being administered to patients.
Aseptic Compounding Technique: Step-by-Step Process
The aseptic compounding process involves several critical steps, including:
- Handwashing and proper gowning, including sterile gloves
- Cleaning and disinfecting compounding environment and laminar airflow hood surfaces
- Arranging sterilized supplies and ingredients in an organized manner
- Mixing and preparing medications carefully following aseptic protocols
- Packaging solutions in sterile plastic containers, followed by careful labeling
- Inspecting, verifying, and documenting that the compounding process adheres to regulations
Challenges and Solutions
While aseptic compounding is critical, maintaining quality can encounter various challenges. Ensuring procedures that produce high-quality pharmaceutical products is essential to overcoming these challenges. Common challenges include contamination risks, procedural errors, and variability in compounding cost. Manufacturers can address these through training, robust process design, continual monitoring, and partnering with an experienced CDMO.
Hazardous Drugs in Aseptic Compounding
Handling hazardous drugs demands additional safety precautions in aseptic compounding. Proper techniques for injection and sterile formulation are crucial when administering drug additives into large volume parenteral solutions to ensure patient safety and medication effectiveness. USP chapter <800> guides necessary safety measures to maintain safe practices.
Packaging and Labeling Sterile Products
Packaging sterile pharmaceutical compounds requires specialized sterile plastic containers and clear labeling to prevent medication administration errors and maintain sterility during storage and transport.
Cost and Efficiency in Aseptic Compounding
Optimizing cost-effectiveness in sterile compounding involves evaluating resource use, consistent training, strategic planning, choosing the right CDMO partner, and employing automated systems when practical.
Collaboration with CDMO Partners
Many pharmaceutical companies collaborate with Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) to meet specific aseptic compounding standards, reduce costs, and guarantee compliance with changing quality regulations. These collaborations are crucial to produce high-quality pharmaceutical products through strict adherence to protocols and validation processes. Experienced CDMOs offer advanced facilities, specialized equipment, and rigorous quality systems improving compounding efficacy.
Future Trends in Aseptic Compounding
Future innovations involve automation technologies, advanced filtration systems, real-time quality control monitoring, and enhanced compounding practices. Keeping updated ensures pharmaceutical companies continue supplying safe compounded sterile medications.
Aseptic compounding is integral in pharmaceutical services, enabling safe preparation of medications while minimizing contamination risks. Adhering to strict guidelines, quality assurance strategies, trained personnel, efficient processes, and partnerships with a knowledgeable CDMO ensures patient safety and quality patient care.
FAQs about Aseptic Compounding
What is the aseptic compounding process?
It is the preparation of sterile medications using techniques and equipment designed to prevent contamination.
What is the difference between sterile compounding and aseptic technique?
Sterile compounding refers to preparations that must be sterile, whereas aseptic technique refers specifically to the methods used to achieve sterility during compounding.
What is aseptic technique in pharmacy?
It involves specific procedures utilized by pharmacists and technicians to maintain sterility, preventing microbial contamination during compounding. The intended purpose of these techniques is to ensure that the sterility of compounded medications is consistently maintained, not just during initial preparation but throughout their shelf life.
What are the 4 aseptic techniques?
Hand hygiene, sterile gloves and gowning, using laminar airflow hoods, and minimizing exposure to contaminants.
What are the 5 principles of aseptic techniques?
Proper hygiene, thorough cleaning, controlled environments, minimized exposure, and sterilization of equipment and supplies.
