Table of Contents
In modern healthcare, innovation in drug delivery systems is reshaping how treatments reach the patient. Among the most impactful of these advancements is the prefilled syringe, a ready-to-use delivery system designed to simplify drug administration, improve patient safety, and enhance treatment outcomes. With growing use in intensive care units, emergency situations, and even home care, prefilled formats are increasingly recognized as one of the fastest growing markets in the pharmaceutical industry. Prefilled syringes are also less costly to manufacture than traditional glass syringes, as manufactures have improved efficiency and reduced material and manufacturing complexities.
Pharmaceutical companies, healthcare providers, and healthcare professionals view prefilled solutions as a way to reduce risk of medication errors, improve compliance, and create cost savings across the manufacturing process and downstream healthcare systems. Pharmaceutical companies and manufactures develop products tailored to the needs of customers and end users, emphasizing the importance of real-time exposure and market acceptance. Consistent quality and regulatory compliance are maintained across multiple production sites to ensure product safety. But to fully understand why prefilled formats have become central to drug delivery, it is important to first define them, review their benefits and limitations, and explore how they are prepared and used.
What Is a Prefilled Syringe (PFS)?
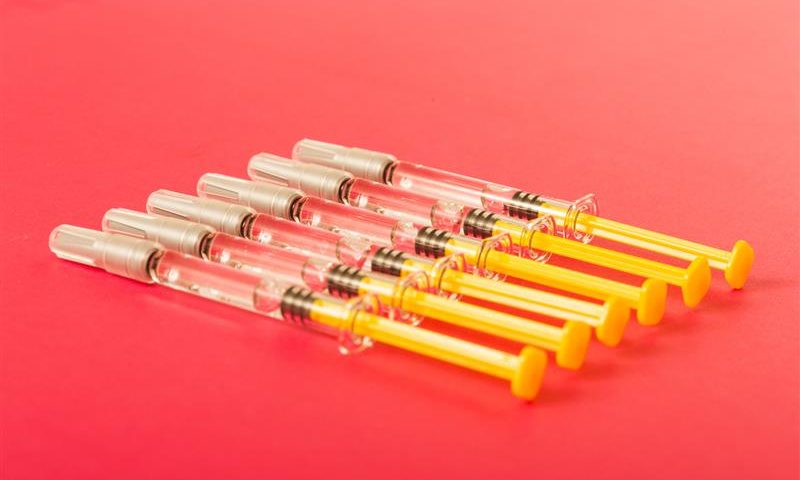
A prefilled syringe (PFS) is a sterile, single-use syringe that comes preloaded with a specific drug dose, designed for injection without requiring prior compounding pharmacies or manual filling by a healthcare provider. Unlike traditional syringe products, which must be filled manually before use, these devices arrive ready to use. Prefilled syringes eliminate the need for vials, reducing overfill requirements and minimizing the risk of contamination compared to traditional vial and syringe systems.
Prefilled formats typically include a syringe needle, plunger, and needle cover, sometimes enhanced with a luer lock or other connecting devices for secure drug delivery system attachment. They may be made from glass syringes or polymer materials, each chosen to optimize shelf life, human factors, and compatibility with biological products. For example, prefilled syringes require less preparation than traditional vial and syringe systems, streamlining the administration process and reducing the potential for medication errors.
The preloaded nature eliminates the need for on-site filling by a compounding pharmacy, minimizes contamination risks, and aligns with stringent ISO standards governing sterile production and fill finish operations. This format offers advantages over the traditional vial, such as reduced drug waste and easier handling for healthcare providers.
Advantages of Prefilled Syringe
The widespread adoption of prefilled syringes can be attributed to their clear benefits across clinical, economic, and patient-centered dimensions:
- Patient Safety and Risk Reduction
By removing manual preparation steps, prefilled formats significantly reduce risk of medication errors such as incorrect dosing, improper dilution, or contamination. This is crucial in intensive care and emergency situations, where delays can mean the difference between recovery and outcomes like cardiac arrest or even cardiac arrest death. Prefilled syringes also enhance efficacy by ensuring accurate dosing and reducing the risk of air bubble introduction during filling. - Ease of Use and Human Factors
Prefilled options are designed with human factors studies in mind, ensuring ease use for healthcare providers and self injection by patients at home. They often include instructions use, ergonomic grips, and optimized needle systems that make administration straightforward. Prefilled syringes allow patients to self administer medication conveniently at home, improving patient compliance and reducing clinical visits. - Reduced Adverse Events and Side Effects
With precise dosing and sterile preparation, prefilled formats limit dosing variability and contamination risks that could may cause allergic reactions, serious side effects, or other adverse events. - Cost Savings and Efficiency
Eliminating the need for a compounding pharmacy for each dose delivers clear cost savings, reduces reliance on compounding pharmacies, and shortens treatment preparation time. Hospitals also save resources by minimizing wastage and relying less on in-hospital syringe systems. For example, vials often require a higher overfill percentage to ensure complete dose withdrawal, while prefilled syringes can be filled more precisely, reducing overfill and improving manufacturing efficiency. - Extended Shelf Life
Advanced materials and sterile manufacturing process enable long shelf life at room temperature, helping maintain important safety information about stability and potency until the expiration date. The availability of high-quality materials and water is essential to support validated manufacturing processes and ensure product safety.
Prefilled syringes are a key innovation in parenteral drug delivery, offering improved safety and convenience for both patients and healthcare providers.
Disadvantages of Prefilled Syringe
While advantages dominate, pharmaceutical companies and healthcare professionals must also weigh the limitations of prefilled solutions:
- Storage and Transport Concerns
Some drugs remain unstable outside refrigeration. While many can be stored at room temperature, others require cold-chain systems to preserve patient safety. Prefilled syringes should not be exposed to direct sunlight, as this can degrade the medicine. Different medicines may require specific storage conditions, and healthcare providers should provide guidance for each type of medicine. - Limited Flexibility
Prefilled syringes provide fixed doses. This limits flexibility in dosing adjustments, especially in intensive care or critical tasks where precise titration is needed. Dosing guidelines for prefilled syringes may differ for pediatric patients and adults, and certain devices are specifically designed for these populations. - Waste Management
Each device requires proper disposal in a sharps disposal container. Widespread adoption necessitates strict sharps disposal protocols to ensure safety and environmental compliance. - Costs in Development
Initial investment in fill finish equipment, adherence to ISO standards, and material design (e.g., glass syringe vs. polymer) can increase development costs. - Possible Side Effects Linked to Needle Design
Certain syringe needle or needle system features may may cause allergic reaction, local irritation at the injection site, or specific side effects like pain during subcutaneous injection.
Prefilled syringes are also widely used for vaccines, offering improved safety and convenience for vaccine administration.
Types and Examples of Prefilled Syringe
Prefilled syringes have transformed the landscape of injectable medications by streamlining the process for a variety of injection types. They are especially impactful for subcutaneous injections, which are commonly used for administering insulin, vaccines, and other medications that require precise dosing and frequent self-administration. By providing a pre-measured dose, prefilled syringes eliminate the need for patients or healthcare providers to draw medication from vials, significantly reducing the risk of medication errors and ensuring that the correct amount is administered every time.
The category of prefilled formats spans different types of syringe products tailored to drug delivery needs:
- Saline Prefilled Syringes & Flush Syringes
Widely used in hospitals to flush IV lines, these ready use devices help prevent clotting and reduce contamination. These syringes are classified as medical devices and must meet strict regulatory standards. - Prefilled Syringes for Biologics
Increasingly used for chronic conditions, these highlight the value of prefillable syringes for biological products requiring precise storage and handling. Prefilled syringes used for biologics are also considered medical devices and are subject to rigorous compliance requirements. - Succinylcholine Chloride Injection & Chloride Injection USP
Common in intensive care and surgical settings, these products demonstrate the need for critical tasks such as muscle relaxation during anesthesia. Misuse may cause serious side effects, so important safety information must always be followed. - Glass Syringes and Pre Filled Syringes
Traditional glass syringes remain preferred for certain formulations, while polymer pre filled syringes are increasingly adopted for stability and portability.
These examples show how syringe systems and syringe injection designs adapt to varied drug delivery requirements, from single dose emergency syringe injection to complex biologics requiring human factors study.
Preparation Method: How to Use Prefilled Syringe
Before starting, gather all the necessary supplies and place them on a flat surface to ensure a clean and stable workspace.
Preparing and using a prefilled format is straightforward, but it requires compliance with important safety information to ensure proper administration:
- Check Expiration Date and Storage
Always verify the expiration date and confirm that the syringe has been stored appropriately, whether refrigerated or at room temperature. - Inspect the Device
Ensure the needle cover is intact, the solution is clear, and there are no cracks in the glass syringe or leaks in polymer designs. - Prepare for Injection
Clean the injection site and remove the needle cover. Use your free hand to gently pinch up the skin at the injection site. Some designs include luer lock connecting device systems for attaching additional components. - Administer the Injection
Follow the instructions use: position the syringe needle. The needle should be inserted into the skin at the appropriate angle, and the plunger should be slowly pushed to deliver the medication. Once the medication has been injected, pull the needle out carefully, keeping the needle straight to minimize discomfort. After removing the needle, apply a cotton ball or gauze to the injection site to stop any bleeding. Deliver the subcutaneous injection, or give subcutaneous injection as directed. Some formats allow patients to self injection, while others require a healthcare provider. - Dispose Right Away
After use, throw away the filled syringe in a disposal container or sharps disposal container to prevent accidental sticks and maintain patient safety. Do not replace the needle cap after use.
Correct preparation and disposal are crucial safety critical tasks that healthcare providers and patients alike must understand. Always follow the prefilled syringe instructions provided with your device and ensure you have all the information needed for safe administration.
Market Trends and Demand for Prefilled Syringe
Globally, prefilled syringes are among the fastest growing markets in the medical device and drug delivery systems space. Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly investing in prefillable syringes to support the rise of biological products, chronic disease treatments, and prefilled medications that enable self injection at home. Demand is particularly high in therapeutic areas requiring emergency administration—such as cardiac arrest or rapid treatment of fluctuating blood pressure—where ready use devices can save lives. At the same time, the convenience of pre filled syringes offers clear cost savings for hospitals by reducing reliance on compounding pharmacies and streamlining workflows for healthcare providers. With regulatory authorities emphasizing compliance with iso standard requirements, and with ongoing innovation in drug delivery systems, market growth is expected to accelerate, making prefilled solutions a cornerstone of modern healthcare.
The prefilled syringe has evolved from a convenience product into a cornerstone of modern drug delivery systems. Its ability to combine patient safety, reliability, and efficiency makes it indispensable in healthcare, from intensive care units to at-home management of chronic conditions. While pharmaceutical companies must address challenges like sharps disposal, shelf life, and production costs, the long-term benefits for both patients and healthcare providers are undeniable.
As regulatory expectations align with ISO standards, and human factors studies continue to refine design, prefilled formats will expand into new therapeutic areas. Whether through pre filled syringe biologics, saline prefilled syringes, or specialized prefilled medications, these devices are set to remain at the forefront of global drug delivery innovation.
FAQs About Prefilled Syringe
What is a prefilled syringe?
A prefilled syringe is a sterile, single dose syringe that comes preloaded with a specific drug dose, eliminating the need for manual preparation by a compounding pharmacy or healthcare provider.
How to inject a prefilled syringe?
Follow the device’s instructions use: remove the needle cover, clean the injection site, position the syringe needle, and deliver the injection (often a subcutaneous injection). Afterward, throw away the filled syringe in a sharps disposal container.
What is the main benefit of using a prefilled medication syringe?
The primary benefit is patient safety. Prefilled devices reduce risk of medication errors, contamination, and dosing mistakes, making them ideal for emergency situations, intensive care, and home use.
What drugs are prefilled syringes?
Examples include Cimzia prefilled syringe, Ajovy prefilled syringe, saline prefilled syringes, flush syringes, and specialty formulations like succinylcholine chloride injection or chloride injection USP. These cover chronic care, acute care, and biological products.