Table of Contents
Pharmaceutical regulations are the foundation of the pharmaceutical industry, ensuring that all drug products meet the highest safety, efficacy, and quality standards. These regulations are crucial for pharmaceutical companies, as they navigate the complex process of bringing new drugs to market while maintaining compliance with global standards. This guide aims to provide an in-depth understanding of pharmaceutical regulations, offering insights into the various frameworks that govern the development, approval, and distribution of pharmaceutical products. Whether you are a newcomer or an industry expert, this comprehensive guide will help you stay informed and compliant in a constantly evolving regulatory landscape.
Understanding Pharmaceutical Regulations
What Are Pharmaceutical Regulations?
Pharmaceutical regulations are a set of laws, guidelines, and standards that govern every aspect of the pharmaceutical industry, from drug development to marketing and sales. These regulations are designed to ensure that pharmaceutical products are safe, effective, and of high quality. Regulatory bodies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe play a significant role in enforcing these regulations, ensuring that all drug products comply with the stringent requirements necessary to protect public health.
The Role of Drug Regulatory Authorities
Drug regulatory authorities are responsible for overseeing the development, approval, and monitoring of pharmaceutical products. These authorities, including the FDA and EMA, ensure that all drug products meet the necessary safety and efficacy standards before they are approved for public use. They also play a critical role in post-market surveillance, monitoring drug safety through adverse event reporting and periodic reviews.
Impact on the Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry is one of the most heavily regulated sectors globally. Pharmaceutical regulations impact every stage of the drug development process, from initial research and development to clinical trials, manufacturing, and marketing. Compliance with these regulations is essential for pharmaceutical companies to avoid legal issues, ensure drug safety, and maintain public trust.
Key Aspects of Pharma Regulatory Compliance
Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP)
One of the most critical components of pharmaceutical regulation is adherence to Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP) guidelines. CGMPs ensure that drug manufacturers follow rigorous standards for product quality, including maintaining clean facilities, properly training employees, and thoroughly documenting manufacturing processes. Compliance with CGMP is mandatory for all pharmaceutical manufacturers, as it helps prevent contamination, ensures product consistency, and guarantees that all drug products are safe for human use.
Ensuring Drug Safety and Efficacy
Ensuring drug safety is a top priority for regulatory authorities. This involves rigorous testing during the drug development process, including preclinical studies and clinical trials, to evaluate the safety and efficacy of new drug products. Regulatory agencies like the FDA require extensive data to demonstrate that a new drug is safe and effective before it can be approved for public use. Post-market surveillance also plays a crucial role in ensuring ongoing drug safety, allowing for the detection of adverse events and the implementation of necessary safety measures.
Compliance with International Standards
Pharmaceutical companies that operate globally must comply with a range of international standards. The International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) plays a key role in harmonizing regulatory standards across different regions. Compliance with these standards ensures that pharmaceutical products meet the necessary quality, safety, and efficacy criteria in multiple markets, facilitating global drug sales and distribution.
Regulatory Guidance and Support
Overview of Regulatory Services
Navigating the complexities of pharmaceutical regulations requires expert regulatory support. Pharmaceutical companies rely on specialized services to ensure compliance throughout the drug development and registration processes. These services include continuous monitoring, evaluation of regulatory information, scientific report writing, risk assessment, and compilation of registration dossiers according to the highest standards. Effective regulatory support is essential for ensuring that all submissions, including new drug applications, variations, and renewals, meet the required regulatory criteria.
Continuous Monitoring and Compliance
Continuous monitoring is a vital component of regulatory compliance. It involves regularly reviewing and updating documentation, assessing regulatory risks, and ensuring that all manufacturing operations adhere to CGMP standards. By maintaining continuous oversight, pharmaceutical companies can proactively address potential compliance issues, minimizing the risk of regulatory delays and ensuring timely market access for their products.
Risk Assessment and Scientific Reporting
Risk assessment is a crucial aspect of regulatory compliance, particularly in areas such as nitrosamines and elemental impurities. Pharmaceutical companies must conduct thorough risk assessments to identify potential hazards and implement measures to mitigate them. Scientific reporting is also essential, as it provides the data needed to support regulatory submissions and demonstrate compliance with safety and quality standards.
FDA Regulations and Guidelines
Overview of FDA Guidelines
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the primary regulatory body for pharmaceutical products in the United States. The FDA’s guidelines cover every aspect of drug development, from preclinical research to post-market surveillance. Compliance with these guidelines is mandatory for all pharmaceutical companies that want to market their products in the United States. The FDA’s guidelines are constantly evolving, so it is essential for pharmaceutical companies to stay up to date with the latest regulatory changes.
The Food and Drug Administration Modernization Act
The Food and Drug Administration Modernization Act (FDAMA) is a significant piece of legislation that introduced several changes to the drug approval process. The FDAMA aimed to streamline the approval process for new drugs, making it faster and more efficient. It also introduced new requirements for post-market surveillance and increased the FDA’s authority to enforce compliance with CGMP guidelines.
Compliance with the Drug Administration Amendments Act
The Drug Administration Amendments Act (DAAA) introduced additional requirements for drug safety and post-market surveillance. The DAAA gave the FDA new tools to monitor drug safety, including the authority to require risk evaluation and mitigation strategies (REMS) for certain drugs. Compliance with the DAAA is essential for ensuring that drug products remain safe and effective throughout their lifecycle.
EMA Regulations and Guidelines
Overview of the European Medicines Agency (EMA)
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is the central regulatory authority responsible for the evaluation, supervision, and safety monitoring of medicines within the European Union. Established in 1995, the EMA plays a crucial role in ensuring that all pharmaceutical products available in the EU meet the highest standards of safety, efficacy, and quality. The agency operates through a centralized drug approval process, allowing pharmaceutical companies to submit a single marketing authorization application that, if approved, is valid across all EU member states. This process is particularly important for innovative and high-impact drugs, ensuring streamlined access to new treatments for patients across Europe. The EMA’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) conducts rigorous scientific assessments to evaluate the benefits and risks of new medicines, ultimately guiding the decision on whether a product should be approved for the European market.
EMA Guidelines and Compliance Requirements
Beyond drug approvals, the EMA provides extensive guidelines and regulatory support to help pharmaceutical companies comply with EU regulations throughout the entire lifecycle of a drug. This includes post-market surveillance through a robust pharmacovigilance system that monitors the safety of medicines once they are available to the public. The EMA also collaborates with national regulatory authorities and international bodies like the FDA to harmonize standards and share critical safety information. For pharmaceutical companies, compliance with EMA regulations is essential not only for gaining market access but also for maintaining the ongoing safety and effectiveness of their products in the European market.
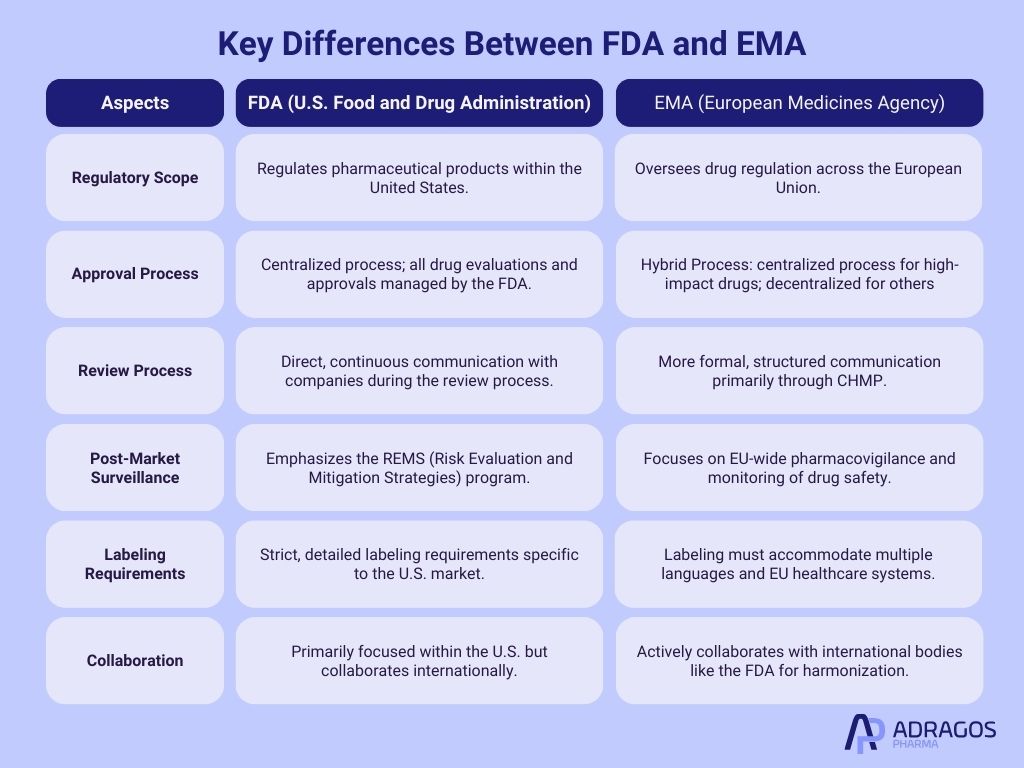
Key Differences Between FDA and EMA
While there is a growing trend toward harmonization, significant differences remain in regulatory approaches between regions. Both FDA and EMA are pivotal regulatory bodies responsible for ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of pharmaceutical products, however they operate within different regulatory frameworks and have distinct processes.
The FDA, as the regulatory authority in the United States, follows a more centralized approach, where all drug approvals and regulations are managed directly by the agency. In contrast, the EMA, which serves the European Union, coordinates with national regulatory agencies across the EU member states, using a centralized process for high-impact drugs, while a decentralized for others, involving national agencies.
Another significant difference lies in their respective review processes: the FDA often engages in more direct communication with pharmaceutical companies during the review phase, allowing for a more iterative process, while the EMA’s evaluation, led by the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), is generally more formalized and structured.
Additionally, the FDA places a strong emphasis on post-market surveillance through its REMS (Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies) program, while the EMA focuses heavily on pharmacovigilance across the EU.
These structural and procedural differences influence how pharmaceutical companies approach drug development, regulatory submissions, and market entry strategies in the U.S. and Europe.
International Pharmaceutical Regulations
Harmonization Through the International Council
The International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) is a key player in the global pharmaceutical regulatory landscape. The ICH works to harmonize technical requirements for drug development and approval across different regions, reducing the need for duplicate testing and streamlining the regulatory process. By adhering to ICH guidelines, pharmaceutical companies can ensure that their products meet the necessary standards for approval in multiple markets.
Compliance with Global Standards
Compliance with global standards is essential for pharmaceutical companies that want to market their products internationally. This includes adhering to the guidelines set by the ICH, as well as complying with regional regulations in the United States, Europe, and other markets. By staying up to date with regulatory changes and working closely with regulatory agencies, pharmaceutical companies can ensure that their products meet the necessary standards for global distribution.
Regulatory Challenges and Solutions
Common Challenges in Pharma Regulatory Compliance
Pharmaceutical companies face several challenges in achieving and maintaining regulatory compliance. These challenges include keeping up with constantly changing regulations, managing the complexity of global regulatory requirements, and ensuring that all documentation is accurate and up to date. Non-compliance with regulatory standards can result in costly delays, fines, and damage to a company’s reputation.
Strategies for Overcoming Regulatory Hurdles
To overcome regulatory challenges, pharmaceutical companies must adopt a proactive approach to compliance. This includes staying informed about regulatory changes, investing in employee training, and working closely with regulatory agencies. By taking a proactive approach to regulatory compliance, pharmaceutical companies can minimize the risk of non-compliance and ensure that their products meet the highest standards of safety and quality.
Pharmaceutical regulations are essential for ensuring that all drug products are safe, effective, and of high quality. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for pharmaceutical companies, as it not only protects public health but also ensures that products can be brought to market efficiently. By staying informed about regulatory changes and working closely with regulatory agencies, pharmaceutical companies can navigate the complex regulatory landscape and bring safe, effective medicines to market.
FAQs about Pharmaceutical Regulations
What regulations do pharmaceutical companies follow?
Pharmaceutical companies must follow a wide range of regulations, including CGMP guidelines, FDA regulations, and international standards set by bodies like the ICH.
What are the 21 CFR guidelines in pharma?
The 21 CFR guidelines are a set of regulations enforced by the FDA that cover various aspects of drug manufacturing, labeling, and distribution to ensure product quality and safety.
What is the pharmacy regulation in the US?
Pharmacy regulations in the US are primarily governed by the FDA and state-level boards of pharmacy, ensuring that all pharmaceutical products meet safety and efficacy standards.
What are the GMP regulations?
Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) regulations are guidelines that ensure that drug products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards.
